Reaction Calorimetry: Customizable Technique for Safe Process Scale-Up
 FAI specializes in characterizing, preventing, and mitigating chemical reactivity hazards. Reaction and adiabatic calorimetry are two laboratory techniques FAI relies on to determine the thermal potential and reactivity of chemical systems. Reaction calorimetry (RC) quantifies the heat evolution and heat evolution rate of a chemical process under the desired reaction conditions. Adiabatic calorimetry does not hold the reaction conditions constant and is generally used to explore the undesired runaway reaction which could be caused by a process deviation such as a loss of cooling, overcharging, or heating by external fire. The undesired reaction(s) commonly have their own heats of reaction which may lead to temperature and/or pressure increases that should be evaluated so that the proper safeguards can be implemented to prevent or mitigate unintended consequences.
FAI specializes in characterizing, preventing, and mitigating chemical reactivity hazards. Reaction and adiabatic calorimetry are two laboratory techniques FAI relies on to determine the thermal potential and reactivity of chemical systems. Reaction calorimetry (RC) quantifies the heat evolution and heat evolution rate of a chemical process under the desired reaction conditions. Adiabatic calorimetry does not hold the reaction conditions constant and is generally used to explore the undesired runaway reaction which could be caused by a process deviation such as a loss of cooling, overcharging, or heating by external fire. The undesired reaction(s) commonly have their own heats of reaction which may lead to temperature and/or pressure increases that should be evaluated so that the proper safeguards can be implemented to prevent or mitigate unintended consequences.
While FAI is well known for our adiabatic testing capabilities using instruments like the FAI-invented Vent Sizing Package (VSP2) and Advanced Reactive System Screening Tool (ARSST), as well as the Accelerated Rate Calorimeter (ARC), we also offer a suite of RC testing capabilities. RC seeks to quantify the total heat of a desired reaction, heat rate of the reaction, and the heat capacity of the reaction mass, with the goal of supporting the safe scale-up of a chemical process. RC data can be used to calculate key process safety parameters, such as the adiabatic temperature rise caused by the desired reaction, to evaluate the potential severity of the reactive hazard and the instantaneous or peak heat generation rates for determining the necessary cooling requirements at process scale. Additionally, RC data can help determine the gas generation rate of a reaction, size important process equipment such as a scrubber for hazardous off-gas and establish the temperature-dependent kinetics of a reaction. Additionally, the thermochemical RC data can be used to optimize process conditions such as process temperature, addition rate, and reagent, catalyst or solvent selection.

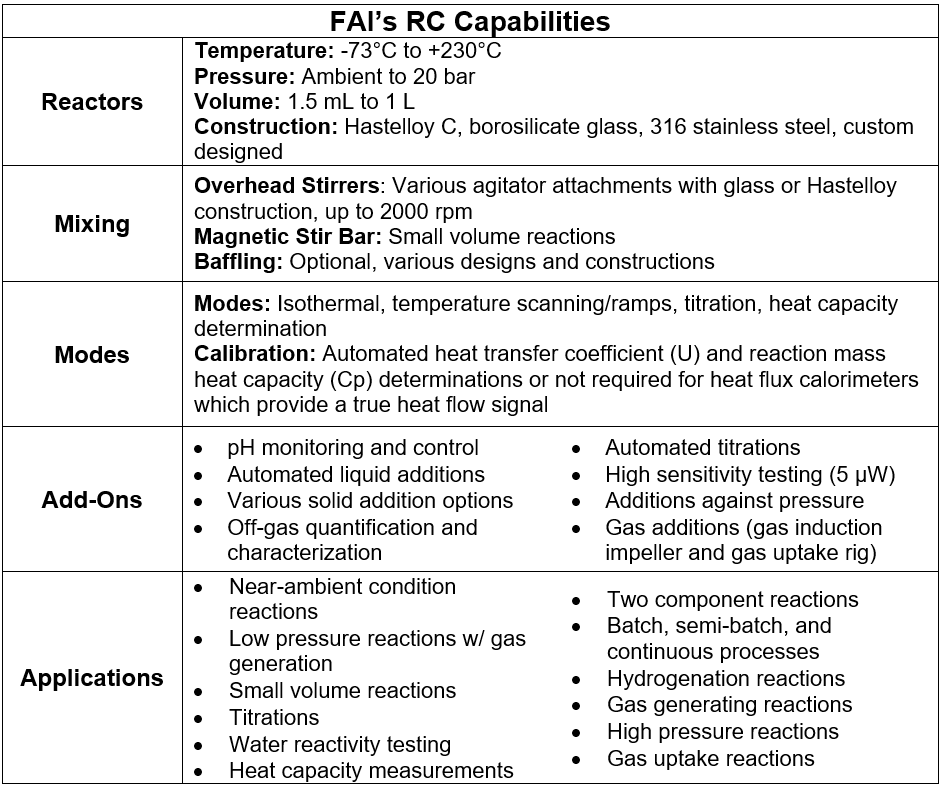
FAI’s RC lab utilizes the Mettler-Toledo RC1, Thermal Hazards Technology (THT) μRC, and/or ChemiSens CPA202 as determined by the system of interest. Our RC instruments are highly customizable allowing for evaluation of a range of processes. Our array of calorimeter configurations allows for flexible experiment design by which we can vary, measure, or control key parameters such as temperature, pressure, wetted material(s) of construction, baffling, agitation type, stir rate, pH, gas generation, and means of dosing (solids, liquids, and gases). Our ability to precisely control testing conditions allows us to study processes that involve flammables, moisture-sensitive, and air-reactive materials and perform chemical compatibility assessments. Please see the table below to better understand how our suite of reaction calorimeters can be tailored to study your process.
In summary, RC data are used to support chemical process scaleup (e.g., determine the cooling requirements for the plant heat exchangers), which results in improved safety, cost efficiency, or sustainability of the chemical processes. We are happy to discuss your new or legacy processes, confirm safe processing conditions, and evaluate other engineering parameters to comply with the OSHA Process Safety Standard 29 CFR 1910.119 and various National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) Standards. Remember that both OSHA and NFPA require the use of recognized and generally accepted good engineering practices (RAGAGEP). RC is considered a RAGAGEP technique for the safer batch and semi-batch chemical reactions processing by providing critical quantitative engineering thermal and kinetic data.
For reaction calorimetry inquiries, please email us at thermalhazardsgroup@fauske.com.


