Fire and Explosion Modeling at Nuclear and Chemical Plants – FATE
By Sara Peters, Fauske & Associates
Having a plan to prevent flammability and explosion hazards in any facility is critical, especially one where there is a risk of toxic material release. Many different variables can affect the progression of these types of events.
It occurred to Fauske & Associates, (FAI) Director of Waste Technology, Jim Burelbach while reading the recent article Fire at Hanford Lab Sends 2 Workers to Hospital that it is not realistic to think that a facility can plan for every possible hazard or risk scenario. That said, a tool that can model building accident response and aid in the development of safer planning can certainly prove invaluable to the process.
One such tool is FATETM (Facility Flow, Aerosol, Thermal, and Explosion Model) software. “FATE software is designed to model general facility volumes (i.e., vaults, hot cells, glove boxes, trenches, lab facilities) as well as radioisotope or any aerosol/contaminant transport. It has been used for design, off-normal, and accident analyses including source term and leak path factor prediction for both nuclear and chemical accidents. Its flexibility to modify the building configuration according to size and regulatory concerns makes it a particularly versatile application for addressing multiple issues that arise in chemical and nuclear facilities,” states Dr. Burelbach.
Developed and maintained under a NQA-1 compliant QA program, FATE is the successor to computer codes used extensively for design and safety analyses for U.S. Department of Energy projects at the Hanford site and elsewhere. It has been used for design, off-normal, and accident analyses including source term and leak path factor prediction for both types of facilities.
As an example, the below graphic illustrates how a nuclear waste storage facility was modeled with FATE at the Hanford site.
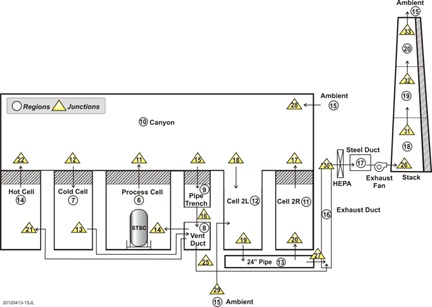
Fortunately, in this incident it appears that thanks to the quick response of a laboratory employee, no radioactive material was involved and the incident was resolved quickly. The fact remains, however, that the hazard exists. You don’t have to choose FATE for your building accident response analyses, but you should consider applying data from some sort of modeling tool when you develop a process safety strategy.
Your facility may have an innovative idea or need to address similar issues for which FATE can be tailored to suit. If you'd like to learn more about FATE, check out FAI's work on the Development of the Source Term Analysis Tool SAS4A-FATE for Lead-and Sodium-Cooled Fast Reactors by clicking below.

